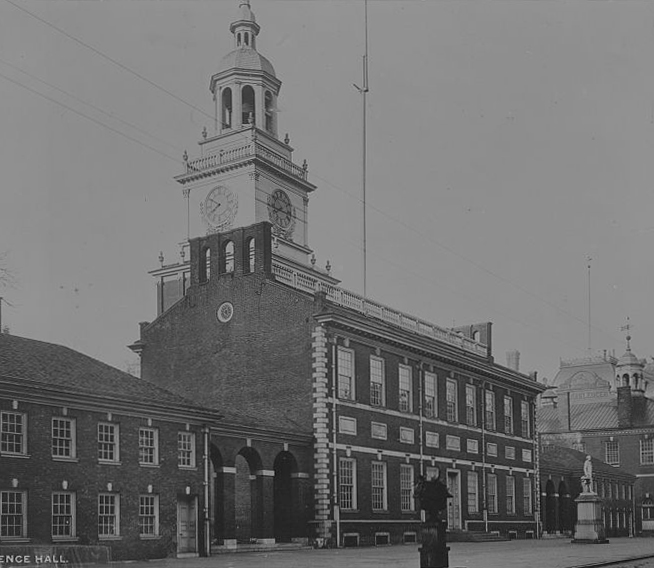
Originally constructed between 1732 and 1753 to house the Pennsylvania Provincial government, the State House (Independence Hall) in Philadelphia was the site of the signings of the Declaration of Independence and the U.S. Constitution.
Revolutionary war begins
On April 19, 1775, shots rang out at Lexington and Concord, Massachusetts, marking the beginning of the American Revolution. The following year on June 7, 1776, Richard Henry Lee presented a resolution to the Second Continental Congress in Philadelphia:
“That these United Colonies are, and of right ought to be, free and independent States, that they are absolved from all allegiance to the British Crown, and that all political connection between them and the State of Great Britain is, and ought to be, totally dissolved.”
Thomas Jefferson drafted the Declaration of Independence during the next three weeks while Congress recessed. After reconvening and making minor changes to the document, Congress officially adopted the Declaration on Independence on July 4, 1776.
 U.S. General Services Administration
U.S. General Services Administration